The Numbers
A number is a mathematical object used to count, meansure and label.
- 0 - Zero
- 1 - One
- 2 - Two
- 3 - Three
- 4 - Four
- 5 - Five
- 6 - Six
- 7 - Seven
- 8 - Eight
- 9 - Nine
Types of Numbers
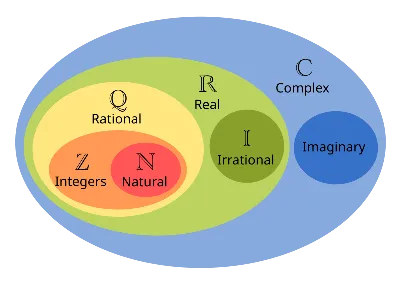
- Natural(): All the whole numbers from one to infinity.
- Integer(): All the whole numbers that can be positive, negative or zero.
- Rational(): All the numbers that are a ratio of two integers.
- Irrational(): All the numbers that aren’t a rational number.
- Real(): All the numbers that can be represented on the number line.
Examples
Rational Numbers
A rational number is any number that can be written as a ratio of two integers.
where:
; ( not equal to )
; ( and are in integers set)
Examples
- (
- ()
- ()
Irrational Numbers
A irrational number is a number that can’t be written as a ratio of two integers.
Examples
is approximately equal to
Real Number Line
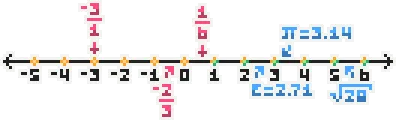
Natural
Integer
Rational
Irrational
The real number line is a visual representation of real numbers used to show their order and magnitude, extending infinitely in both directions.