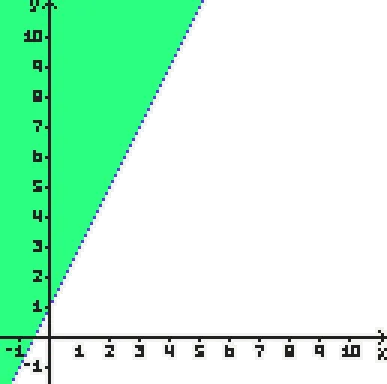
y > 2x + 1
Linear inequalities represent a region of a plane, where the solutions are the values of the variable(s) that satisfy the inequality.
Key Characteristics of Linear Inequalities
Degree of 1 : The highest power of any variable is 1.No products of variables : There are no terms like xy, x²y, x², y², or similar combinations.Boundary Line : When plotted on a coordinate plane, it forms a straight line. This line represents the equality part of the inequality.Shaded Region : The solution to the inequality is represented by a shaded region on the coordinate plane. Examples of Linear Inequalities 2 x + 3 y > 7 2x + 3y > 7 2 x + 3 y > 7 y ≤ 5 x − 2 y ≤ 5x - 2 y ≤ 5 x − 2 x ≥ 4 x ≥ 4 x ≥ 4
Examples of Non-linear Inequalities x 2 + y 2 ≤ 25 x² + y² ≤ 25 x 2 + y 2 ≤ 25 y > 2 x 3 − 1 y > 2x³ - 1 y > 2 x 3 − 1 1 / x + y < 3 1/x + y < 3 1/ x + y < 3
Solving Linear Inequalities 7 x − 3 < 11 7 x − 3 + 3 < 11 + 3 7 x < 14 7 x 7 < 14 7 7 7 < 14 7 x < 2 7x - 3 < 11\\
7x - 3 + 3 < 11 + 3\\
7x < 14\\
\frac{7x}{7} < \frac{14}{7}\\
\frac{\cancel{7}}{\cancel{7}} < \frac{14}{7}\\
x < 2 7 x − 3 < 11 7 x − 3 + 3 < 11 + 3 7 x < 14 7 7 x < 7 14 7 7 < 7 14 x < 2
3 ( x − 3 ) ≥ − 2 x + 6 3 x − 9 ≥ − 2 x + 6 3 x − 9 + 9 ≥ − 2 x + 6 + 9 3 x ≥ − 2 x + 15 3 x + 2 x ≥ − 2 x + 2 x + 15 5 x ≥ 15 5 x 5 ≥ 15 5 5 x 5 ≥ 15 5 x ≥ 3 3(x-3) \ge -2x + 6\\
3x - 9 \ge -2x + 6\\
3x - 9 + 9 \ge -2x + 6 + 9\\
3x \ge -2x + 15\\
3x + 2x \ge -2x + 2x + 15\\
5x \ge 15\\
\frac{5x}{5} \ge \frac{15}{5}\\
\frac{\cancel{5}x}{\cancel{5}} \ge \frac{15}{5}\\
x \ge 3 3 ( x − 3 ) ≥ − 2 x + 6 3 x − 9 ≥ − 2 x + 6 3 x − 9 + 9 ≥ − 2 x + 6 + 9 3 x ≥ − 2 x + 15 3 x + 2 x ≥ − 2 x + 2 x + 15 5 x ≥ 15 5 5 x ≥ 5 15 5 5 x ≥ 5 15 x ≥ 3
x + 8 4 < − 2 x − 7 4 ∗ x + 8 4 < 4 ( − 2 x − 7 ) 4 ∗ x + 8 4 < 4 ( − 2 x − 7 ) x + 8 < − 8 x − 28 x + 8 − 8 < − 8 x − 28 − 8 x < − 8 x − 36 1 x + 8 x < − 8 x + 8 x − 36 9 x < − 36 9 x 9 < − 36 9 9 x 9 < − 36 9 x < − 4 \frac{x+8}{4} < -2x - 7\\
4 * \frac{x+8}{4} < 4(-2x - 7)\\
\cancel{4} * \frac{x+8}{\cancel{4}} < 4(-2x - 7)\\
x+8 < -8x - 28\\
x+8-8 < -8x - 28-8\\
x < -8x - 36\\
1x + 8x < -8x + 8x - 36\\
9x < -36\\
\frac{9x}{9} < \frac{-36}{9}\\
\frac{\cancel{9}x}{\cancel{9}} < \frac{-36}{9}\\
x < -4 4 x + 8 < − 2 x − 7 4 ∗ 4 x + 8 < 4 ( − 2 x − 7 ) 4 ∗ 4 x + 8 < 4 ( − 2 x − 7 ) x + 8 < − 8 x − 28 x + 8 − 8 < − 8 x − 28 − 8 x < − 8 x − 36 1 x + 8 x < − 8 x + 8 x − 36 9 x < − 36 9 9 x < 9 − 36 9 9 x < 9 − 36 x < − 4
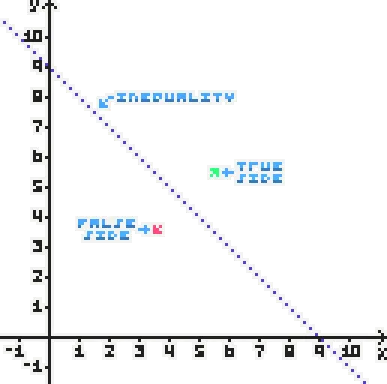
Graphing Linear Inequalities The best way to graph a linear inequality is to write the inequality in slope-intercept form, then test the inequality to determine which side of the line to shade.
y = m x + b y = mx + b y = m x + b
Graph Line Depending on the inequality operator used, the line in the graph will be solid or dashed:
≥ \ge ≥ ≤ \le ≤ > > > < < < Graphing Inequalities (youtube) Graphing two variable inequality (youtube)
Examples
2 ( x + 10 ) ≤ 30 2 x + 20 ≤ 30 y ≥ 2 x + 20 2(x + 10) \le 30\\
2x + 20 \le 30\\
y \ge 2x + 20 2 ( x + 10 ) ≤ 30 2 x + 20 ≤ 30 y ≥ 2 x + 20
6 x + 3 y > 9 6 x − 6 x + 3 y > − 6 x + 9 3 y > − 6 x + 9 3 y 3 > − 6 x + 9 3 3 y 3 > − 6 x + 9 3 y > − 2 x + 3 6x + 3y > 9\\
6x - 6x + 3y > -6x + 9\\
3y > -6x + 9\\
\frac{3y}{3} > \frac{-6x+9}{3}\\
\frac{\cancel{3}y}{\cancel{3}} > \frac{-6x+9}{3}\\
y > -2x + 3 6 x + 3 y > 9 6 x − 6 x + 3 y > − 6 x + 9 3 y > − 6 x + 9 3 3 y > 3 − 6 x + 9 3 3 y > 3 − 6 x + 9 y > − 2 x + 3
− 2 x − 2 y ≥ 2 x + 4 − 2 x + 2 x − 2 y ≥ 2 x + 2 x + 4 − 2 y ≥ 4 x + 4 − 1 ∗ − 2 y ≥ − 1 ( 4 x + 4 ) 2 y ≤ − 4 x − 4 2 y 2 ≤ − 4 x − 4 2 2 y 2 ≤ − 4 x − 4 2 y ≤ − 2 x − 2 -2x - 2y \ge 2x + 4\\
-2x + 2x - 2y \ge 2x + 2x + 4\\
-2y \ge 4x + 4\\
-1 * -2y \ge -1(4x+4)\\
2y \le -4x - 4\\
\frac{2y}{2} \le \frac{-4x-4}{2}\\
\frac{\cancel{2}y}{\cancel{2}} \le \frac{-4x-4}{2}\\
y \le -2x - 2 − 2 x − 2 y ≥ 2 x + 4 − 2 x + 2 x − 2 y ≥ 2 x + 2 x + 4 − 2 y ≥ 4 x + 4 − 1 ∗ − 2 y ≥ − 1 ( 4 x + 4 ) 2 y ≤ − 4 x − 4 2 2 y ≤ 2 − 4 x − 4 2 2 y ≤ 2 − 4 x − 4 y ≤ − 2 x − 2