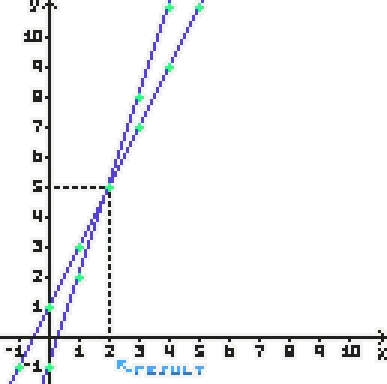
2x+1=3x−1
A linear equation is an equation that describes a relationship with a constant rate of change, forming a straight line.
Key Characteristics of Linear Equations
- Degree of 1: The highest power of any variable is 1.
- No products of variables: There are no terms like xy, x2y, or similar combinations.
- Straight line graph: When plotted on a coordinate plane, it forms a straight line.
Examples of Linear Equations
2x+3y=7
y=5x−2
x=4
Examples of Non-linear Equations
x2+y2=25
y=2x3−1
1/x+y=3
Solving Linear Equations
A great way to master linear equations is by practicing:
GeoGebra - Linear Equation Generator
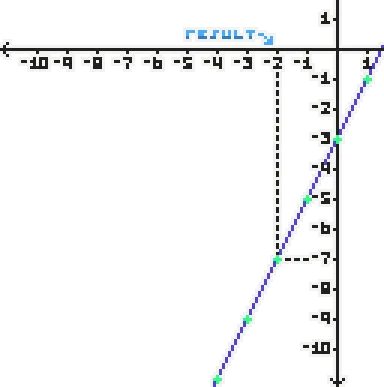
2x−3=−7
2x−3=−72x−3+3=−7+32x=−422x=2−422x=2−4x=−2
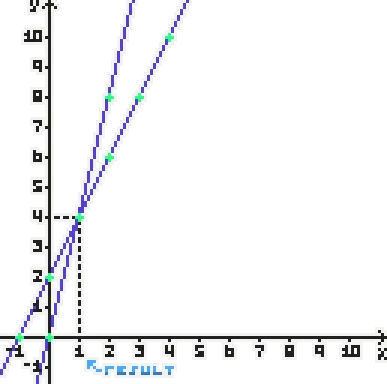
x(3+1)=2(x+1)
x(3+1)=2(x+1)3x+x=2x+24x=2x+24x−2x=2x−2x+22x=222x=2222x=22x=1
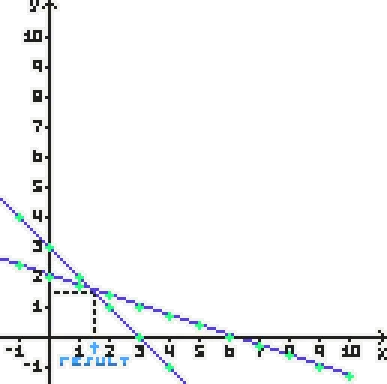
3−x+6=−x+3
3−x+6=−x+33∗3−x+6=3(−x+3)3∗3−x+6=3(−x+3)−x+6=−3x+9−x+6−6=−3x+9−6−x=−3x+3−x+3x=−3x+3x+32x=322x=2322x=23x=1.5
Graphing Linear Equations

The best way to graph a linear equation is to write the equation in slope-intercept form.

y=mx+b
Graphing Linear Equations (youtube)
Graphing Linear Equations in Two Variables (palmbeachstate.edu)
Examples
4x−7=21y=4x−7
7x+9=3(x+2)+1y1=7x+9y2=3x+7
y−5x=x+5y−5x+5x=5x+1x+5y=6x+5
3x+4y=183x−3x+4y=−3x+184y=−3x+1844y=4−3x+1844y=4−3x+18y=4−3x+18





